Indian Military Operations Along LoC Result in Over 100 Pakistani Soldier Casualties: DGMO Lt Gen Rajiv Ghai
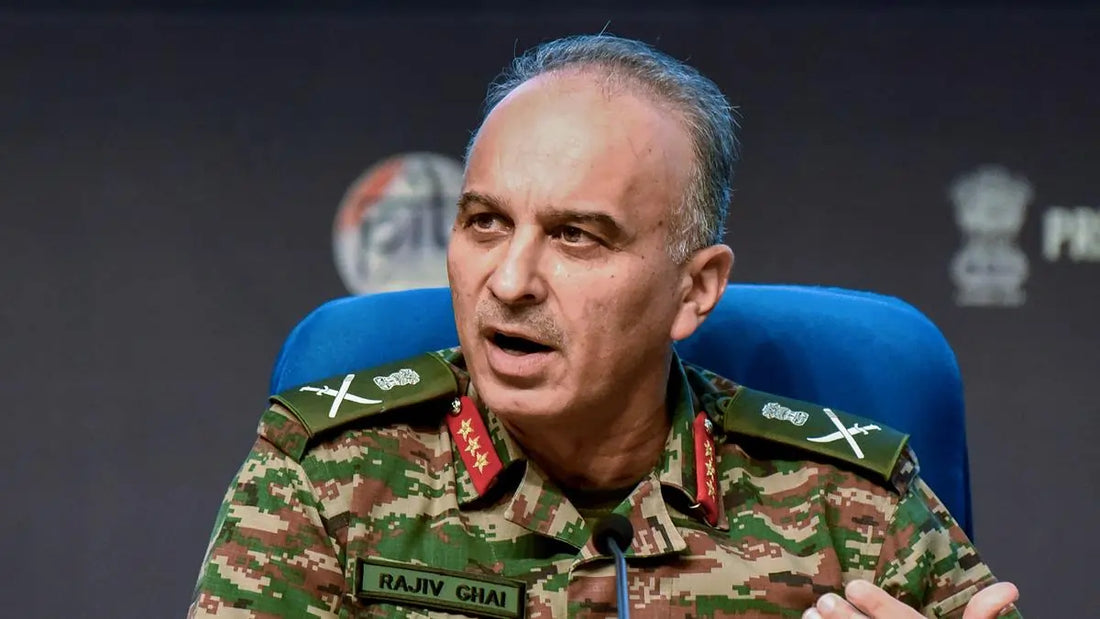

Director General of Military Operations (DGMO) Lt Gen Rajiv Ghai announced on Tuesday that over 100 Pakistani soldiers were killed in India's precision operations along the Line of Control (LoC) following the Pahalgam terror attack. Speaking at the United Nations Troop Contributing Countries (UNTCC) conclave held at the Manekshaw Centre in Delhi, he characterized the operations as a swift and measured response that demonstrated India's evolving military strategy, which integrates precise military action with diplomatic and economic strategies.
Lt Gen Ghai noted that Pakistan's own acknowledgments, including the awarding of posthumous gallantry medals on August 14, suggest that the casualties exceeded 100 soldiers. He elaborated that India targeted nine sites within Pakistan, utilizing a combination of military precision, diplomatic agility, informational dominance, and economic tactics. As part of this broader strategic approach, India also temporarily suspended the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960.
Addressing the Army chiefs from 30 nations, the DGMO underscored that Indian forces were thoroughly prepared for any potential Pakistani retaliation. "It would be naive to think the Indian Army would undertake such operations without planning for possible counteractions. We had anticipated several moves in advance," he remarked, explaining that additional targets along the LoC were engaged in preparation for cross-border fire.
The operations prompted Pakistan to seek an end to hostilities within 88 hours, highlighting the effectiveness and decisiveness of India's actions. Lt. Gen. Ghai also highlighted the readiness of the Indian Navy, which was well-positioned in the Arabian Sea to escalate the conflict if necessary.
Regarding the terrorists responsible for the Pahalgam attack, he confirmed that they were located and neutralized within 96 days. He described this outcome as "clinical," affirming that justice had been served.