Comprehensive Guide to Indian Army Ranks: Insignia and Roles for Officers, JCOs, and NCOs
The Indian Army stands as a fundamental component of the country's national security, recognized for both its bravery and elaborate organizational framework. At the core of this structure is the rank system, segmented into three main categories: Commissioned Officers, Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs), and Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs). Each rank is indispensable, facilitating operational effectiveness, maintaining discipline, and ensuring a clear command chain vital for military functionality. This detailed overview examines these ranks, their respective insignia, roles, and the significance of this hierarchy for those aspiring to join the armed forces.
Historical Context
The evolution of the Indian Army's structure and rank system spans centuries, with significant changes post-Independence. The establishment of a well-organized military was prioritized, leading to the adoption of a comprehensive rank system akin to those of prominent global military forces. This system not only outlines the hierarchy but also supports discipline and order, crucial for military operations. Over the years, the responsibilities associated with each rank have expanded to meet the demands of modern warfare and defense strategies.
Understanding the Ranks of the Indian Army
Commissioned Officers
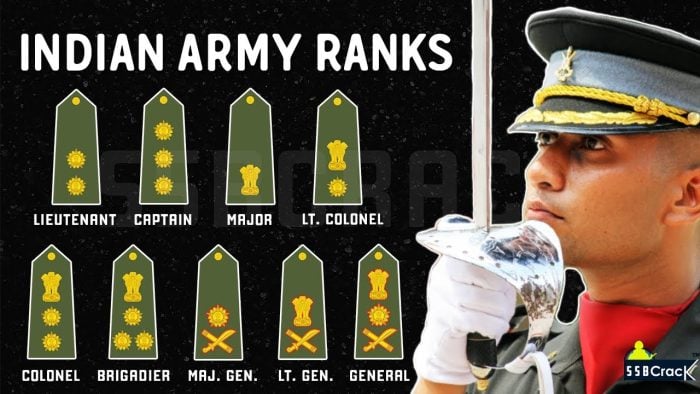
Commissioned Officers are pivotal to military leadership, responsible for key decisions and strategic command. Each rank entails specific duties and leadership responsibilities, requiring significant training and education.
| Rank | Description | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Field Marshal | Highest rank, awarded for extraordinary service. | Symbolizes unparalleled contributions to military strategy and national service. |
| General | Highest active rank, leads the Indian Army. | Formulates and implements military strategy, oversees all divisions. |
| Lieutenant General | Oversees corps and large formations. | Engages in high-level decision-making in national defense. |
| Major General | Commands divisions. | Tactical planning and execution across large regions. |
| Brigadier | Commands brigades. | Manages resources and personnel effectively. |
| Colonel | Commands battalions and regiments. | Influences training and operational readiness. |
| Lieutenant Colonel | Functions as executive officer within battalions. | Oversees operational tasking and command implementation. |
| Major | Leads a company or smaller units. | Works closely with junior officers and enlisted personnel. |
| Captain | Leads platoons. | Immediate decision-maker at the tactical level. |
| Lieutenant | Junior officer, commands small teams. | Implements commands and direct leadership. |
Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs)
Serving as a crucial link between Commissioned Officers and NCOs, JCOs play important leadership roles and provide technical expertise, ensuring effective communication and operational execution.
| Rank | Insignia | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Subedar Major | Gold national emblem with a stripe. | Senior-most JCO, aids in administration and liaising. |
| Subedar | Two gold stars with a stripe. | Commands sections or squadrons, instills discipline. |
| Naib Subedar | One gold star with a stripe. | Assists in troop management and supports the Subedar Major. |
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs)
NCOs are fundamental to the Indian Army, responsible for training and maintaining discipline among soldiers to ensure the required standards for operational efficiency.
| Rank | Insignia | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Havildar | Three chevrons. | Leads a section, manages training and soldiers. |
| Naik | Two chevrons. | Supervises squads, assists in training. |
| Lance Naik | One chevron. | Junior leadership, assists higher ranks. |
| Sepoy | No insignia. | Frontline soldier, executes orders. |
Key Facts and Figures
The Indian Army comprises 17 distinct ranks across three categories: Commissioned Officers, JCOs, and NCOs. Promotion to JCO ranks depends on merit and seniority, ensuring leadership by the most capable. Each rank fulfills specialized roles, from frontline duties by Sepoys to strategic planning by Generals. Insignia worn by soldiers signify their experience, rank, and authority, establishing a clear hierarchy.
The Importance of Understanding Indian Army Ranks
For those aspiring to join the Indian Army, understanding the rank structure is essential. It aids in navigating military education and training, preparing candidates for their future responsibilities. Knowledge of ranks is also crucial for competitive exams, with resources available to aid aspirants.
Real-world Applications of the Rank Structure
Familiarity with the rank structure is crucial for career progression and engaging with superiors. The hierarchy ensures clear responsibilities and a path for advancement based on merit and performance. Understanding the roles associated with each rank helps in developing leadership skills and enhancing teamwork for military missions.
Challenges and Solutions
A key challenge faced by candidates is misunderstanding the significance of ranks, leading to confusion during training. Solutions include enhanced training programs and mentorship systems to foster understanding and leadership values.
Future Trends and Predictions
As warfare and military operations evolve, the rank structure may undergo adjustments. Technological advances and new strategies could shift responsibilities within ranks, emphasizing tech-savvy abilities. The Indian Army also aims to enhance inclusivity, which may lead to modifications in ranks and gender roles.
Conclusion
The rank structure of the Indian Army embodies the principles of discipline, responsibility, and leadership. Each rank plays a specific role, contributing to the military's overall efficacy and operational readiness. Understanding these ranks is a crucial step for those aiming to succeed in military service. Resources are available to aid future leaders in comprehending the intricacies of army ranks, enhancing operational efficiency, and strengthening national security. By gaining a deeper understanding of this structure, aspirants can better prepare for their roles as protectors of India's sovereignty.



















