Indian Army Ranks List - Insignia, Officers, JCOs, NCOs
The Indian Army, a crucial pillar of the nation's defence, operates under a structured rank system that reflects its organizational discipline and operational efficiency. Understanding the hierarchy of Indian Army ranks is essential for anyone interested in military service, whether as a career choice or as a matter of national pride. This article delves into the various ranks within the Indian Army, detailing the roles, responsibilities, and insignia associated with each level.
🚀 Order Now – SSB Interview Books Power Pack: 4 Essential Books for Defence Aspirants
Overview of Indian Army Ranks
The Indian Army ranks are categorized into three primary groups:
- Commissioned Officers
- Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs)
- Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs)
Each category plays a vital role in the operational structure of the army, ensuring that commands flow smoothly from the highest levels of authority down to the soldiers on the ground. The rank structure has been influenced by Western military systems, particularly those of the British and Commonwealth nations.
Importance of Ranks
The ranks within the Indian Army serve multiple purposes:
- Hierarchy: Establishes a clear chain of command.
- Responsibility: Defines the roles and duties assigned to personnel at each level.
- Recognition: Acts as a badge of honor, denoting the level of expertise and leadership.
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers are the backbone of the Indian Army's leadership. They are responsible for commanding units and making strategic decisions. The ranks of commissioned officers, from highest to lowest, include:
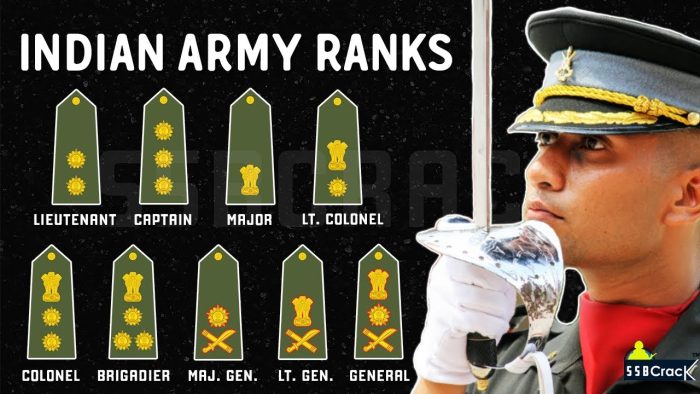
| Rank | Insignia Description |
|---|---|
| Field Marshal | National emblem over a crossed sword and baton, encircled by a lotus blossom wreath. |
| General | National emblem over a five-pointed star, above crossed sword and baton. |
| Lieutenant General | National emblem above crossed sword and baton. |
| Major General | A five-pointed star above crossed sword and baton. |
| Brigadier | National emblem above three five-pointed stars arranged in a triangle. |
| Colonel | National emblem above two five-pointed stars. |
| Lieutenant Colonel | National emblem above a single five-pointed star. |
| Major | National emblem. |
| Captain | Three five-pointed stars in a row. |
| Lieutenant | Two five-pointed stars in a row. |
Roles and Responsibilities
- Field Marshal: This is an honorary title awarded for exceptional service. The role is largely ceremonial, with no active operational responsibilities.
- General: The Chief of Army Staff, responsible for the entire army's strategic direction and operational readiness.
- Lieutenant General: Commands corps-level operations, overseeing multiple divisions.
- Major General: Typically in charge of division-level operations, responsible for tactical and operational planning.
- Brigadier: Leads brigades and manages multiple battalions, focusing on operational execution.
- Colonel: Commands a full battalion, ensuring readiness and discipline among troops.
- Lieutenant Colonel: Often serves as the second-in-command in a battalion or leads smaller units.
- Major: Oversees companies and contributes to planning at the battalion level.
- Captain: Commands a company, responsible for tactical operations and troop welfare.
- Lieutenant: The entry-level officer rank, leading a platoon and managing day-to-day operations.
Junior Commissioned Officer Ranks
Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs) serve as a critical link between commissioned officers and non-commissioned officers. They bring valuable experience and leadership to their roles. The ranks of JCOs include:
| Rank | Insignia Description |
|---|---|
| Subedar Major | Gold national emblem with a stripe. |
| Subedar | Two gold stars in a row with a stripe. |
| Naib Subedar | One gold star with a stripe. |
Role of JCOs
- Subedar Major: Senior-most JCO, assisting in administrative and operational tasks within a battalion.
- Subedar: Commands sections or squadrons, ensuring discipline and operational effectiveness.
- Naib Subedar: Assists in managing troops and supports the Subedar Major in various duties.
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) are the backbone of the Indian Army, responsible for training, discipline, and the welfare of soldiers. Their ranks include:
| Rank | Insignia Description |
|---|---|
| Havildar | Three chevrons. |
| Naik | Two chevrons. |
| Lance Naik | One chevron. |
| Sepoy | No insignia. |
Responsibilities of NCOs
- Havildar: Leads a section, responsible for training and managing soldiers.
- Naik: Supervises squads and assists in training junior soldiers.
- Lance Naik: A junior supervisory role, assisting higher ranks in executing orders.
- Sepoy: The basic soldier rank, performing frontline duties and executing commands.
The Path to Joining the Indian Army
For those aspiring to serve in the Indian Army, understanding the rank structure is crucial. The recruitment process typically involves:
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must meet specific educational and physical standards.
- Entrance Exams: Various exams such as the NDA (National Defence Academy) and CDS (Combined Defence Services) are conducted.
- Training: Successful candidates undergo rigorous training at esteemed military academies.
Preparing for a Career in the Indian Army
Aspiring candidates must focus on:
- Physical Fitness: Regular exercise and physical training to meet the army's standards.
- Educational Qualifications: Completing necessary educational requirements for the desired rank.
- Mental Preparedness: Developing resilience and leadership qualities essential for military service.
Conclusion
The Indian Army ranks system is a structured hierarchy that plays a vital role in maintaining discipline and operational efficiency. Each rank, from commissioned officers to non-commissioned officers, carries specific responsibilities and insignia that symbolize authority and service. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for anyone considering a career in the Indian Army, as it reflects not only the organizational structure but also the values of leadership, dedication, and service to the nation.
FAQs
What are the main categories of ranks in the Indian Army?
The Indian Army ranks are categorized into three main groups: Commissioned Officers, Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs), and Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs).
How many ranks are there in the Indian Army?
There are a total of 17 ranks in the Indian Army, ranging from Field Marshal at the top to Sepoy at the bottom.
What is the highest rank in the Indian Army?
The highest rank in the Indian Army is Field Marshal, which is an honorary title awarded for exceptional service.
What roles do Junior Commissioned Officers play?
Junior Commissioned Officers serve as a bridge between commissioned officers and non-commissioned officers, managing troops and ensuring operational efficiency.
How can one join the Indian Army?
Joining the Indian Army typically involves meeting eligibility criteria, passing entrance exams, and undergoing training at military academies.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Army ranks, their significance, and the pathways to joining this esteemed organization. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone aspiring to serve their country in the military.




















